Instructions: This page calculates Pin-in-Paste stencil metrics if preforms are used. The first column contains PWB and component inputs, it also contains input boxes if rectangular pins or stencil apertures are used. Below the "If Pin is Rectangular..." input boxes are the preform inputs. The Stencil Metrics section contains the calculations for the dimensions of the stencil's apertures required for the needed solder paste volume. The first five boxes under Stencil Metrics are for rectangular apertures and the last five boxes are for dogbone apertures.

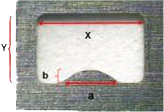
Initial work by Gervascio etali refined by McLenaghanii was performed to estimate the volume of the fillet in the pin-in-paste process. The assumption was made that the cross section of the fillet could be described by the radius of a circle as shown in Figure 1.

Simple geometry will show that the area of one side of the cross section of the fillet is equal to the 0.215r2, let's call this area A. Pappus of Alexandria circa 300 b.c., developed the concept of a volume of revolution. His work was refined in the 1500s by the Dutchment Guldin. What they showed was that if one takes an areal cross section such as A, it is possible to calculate the volume of the body by mathematically revolving it around the central axis. If one does this by using calculus, it can be shown that the resulting volume is equal to:
V = 2Π A xc
Where xc is called the centroid of that cross sectional area. For our fillet, calculus will show that:
xc = 0.2234r + a, hence the volume of one fillet is: V = 2Π(0.215r2)(0.2234r + a)
i Gervascio, T, Proceedings of SMTAI, pp 333-340, 1994, San Jose